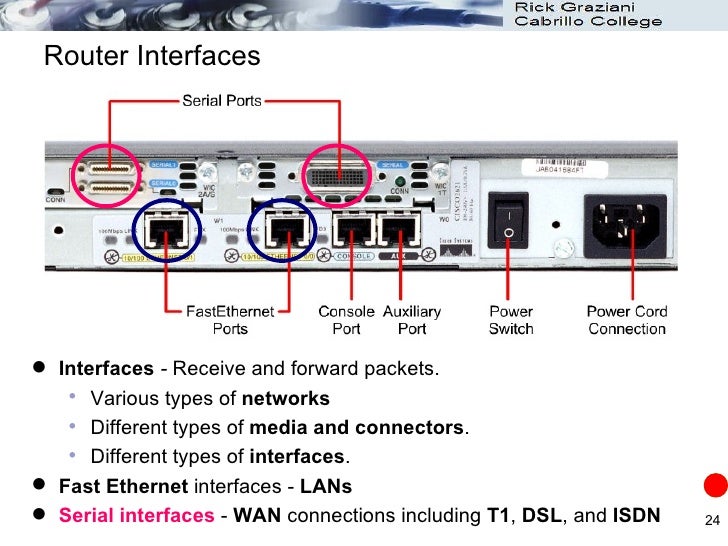
Ethernet is principally designed for local area networking, and runs at speeds of 10, 100, 1000 Mbit/sec and more, and normally is for links of up to about 100 metres, though you can go further with fibre or various kinds of extenders. And as Zac reminded me - how could we forget? - ethernet is effectively a bus connecting many-to-many (and physically a bus topology in its older incarnations such as 10base2.)Serial links are normally X.21 and are principally designed for longer point-to-point networking, such as provided by a telephone company leased line, and are often around 64 kbit/sec, 2M bit/sec, 34 Mbit/sec (standards vary by country, distance and price). A leased line would typically be many kilometres.In packet tracer, sometimes you use those links just because you have them. If the routers are adjacent, you can use whichever you like.In real life, you choose which you're using predominantly on distance and what kinds of links you have available in your locale.The ordinary serial interfaces on Cisco routers are synchronous.Additionally there are also asynchronous serial lines, usually RS-232, such as are on the console and aux ports.
Occasionally you see RS-422 for longer async lines, or 4-20 mA loops. On a computer these would normally just be called 'serial ports' as sync serial is extremely unusual on computers. Usually these are used for character-by-character communication, such as configuration.
But you can also run packet communication over them, with PPP and similar protocols. With direct wired connections, these are usually up to a few tens of metres; with modems these can be global. Speeds are in comparison very slow, ranging from about 300 bit/sec to about 115.2 kbit/sec.
In addition to jonathanjo's answer: the main difference in usage is that serial connections are always point-to-point - a serial interface doesn't require any addressing, it is often 'unnumbered'. Note that network (IP) packets still carry addresses but on a serial interface, the data-link layer barely exists and the frames themselves don't carry addresses.While (modern) Ethernet is also point-to-point on the physical layer, Ethernet frames do require addressing - they carry a source and a destination MAC address for the data-link layer. This allows for layer-2 point-to-multipoint connections and L2-processing/forwarding behind the immediate physical interface - essentially an L2-transparent connection between switches.You can very well configure multiple Ethernet ports in the exact same way (esp. By putting them in a common VLAN) but you can't do that with serial ports because there is no link-layer addressing between them. In other words, serial ports require layer-3 configuration (at least a routing table entry) while Ethernet ports do not.
Although the RS-323 interface driven by a UART chip may be banging out the bits one at a time, the actual encoding done by the modem may use parallel encodings whereby multiple bits are transmitted at the same time. Ethernet also used to be strictly serial (baseband pulses at a rate of 10 Mhz). Modern Ethernet protocols are not serial. Jul 30, 2011 Some Ethernet networks use coaxial cables, but that’s rarer, and present in rather large LANs, which span over areas between buildings. If you want to see what a coaxial cable is like, look at the thick cable that links your TV antenna to your TV set.
An Ethernet is primarily a group of LAN technologies which are covered in IEEE 802.3 u standard. The ethernet is easily maintained and managed and considered to be low-cost network implementation solution.
It comes in three variations, 10Base-T ethernet, fast ethernet and gigabit ethernet. The main difference between fast ethernet and gigabit ethernet is the contradicting speed where fast ethernet provides at maximum 100 Mbps of data transmission speed whereas gigabit ethernet offers high-speed data transmission up to 1 Gbps.
Definition of Fast EthernetThe fast Ethernet was devised under the name of 802u to contend for LAN protocol FDDI. It is completely based on 10-Base-T ethernet as it is a successor of 10-Base-T Ethernet.
It was popular because it is simple to implement, manage and maintain. The fast ethernet has the advantage of backward compatibility. It is ten times faster than its successor and is capable of providing data speed of 100 Mbps.聽There are three varieties of fast ethernet – 100Base-T4, 100Base-Tx and 100Base-Fx.MAC layer of fast ethernet is different from the standard ethernet where the data rate and collision domain are altered. The data rate is incremented by the factor of 10 and collision rate is decremented by the factor of 10. Although, there exhibit no change in frame format, then how did it achieve ten times faster speed without changing frame format? To accomplish this, the RTT (Round trip time) has reduced from 57.6 to 5.76 microseconds.The time needed for a signal pulse or a packet to traverse from a certain source to a particular destination and return from there again is known as Round trip time or Round-trip delay.
Definition of Gigabit EthernetThe Gigabit Ethernet was devised to provide a higher rate of transmission up to 1 Gbps.聽The prior intention was to develop a technology that can properly work on existing networking equipment.聽It is constructed on the top of the Ethernet protocols such as CSMA/CD. Both the modes full duplex and half duplex are supported by it, similar to fast ethernet.In the beginning single-mode, multi-mode fibre and short-haul coax cable are used. After that, twisted pair cable standards were also included. Gigabit rates are achieved by using physical channel technology as a standard over the optical fibres.The important improvements or changes in Gigabit Ethernet from its predecessor are depicted below:. Andreas vollenweider white winds rar.
The fibre optic cable is majorly used instead of coaxial cable and twisted pair cable. MAC layer has also modified in gigabit ethernet. It uses carrier extension to detect frames coming from a larger distance. To manage flow control the X-on/X-off protocols are used, that work over any of the full-duplex Ethernet.
This helps in stopping the transmission when a switch buffer is near to its capacity. The quality of service (QoS) is supported by gigabit ethernet with the help of signalling scheme so that the real-time packets get the better treatment. Key Differences Between Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet. The data rate provided by fast ethernet is up to 100 Mbps. On the other hand, gigabit ethernet offers up to 1 Gbps speed.
As the speed is increased in Gigabit ethernet, so the delay is decreased whereas the fast ethernet generates more delay. The configuration of fast ethernet is simpler than gigabit ethernet. The distance covered by fast ethernet is at most 10 km.
On the contrary, the gigabit ethernet covers 70 km. Round trip delay of fast ethernet is 100-500 bit times. As against, gigabit ethernet has the delay of 4000 bit times.ConclusionFast Ethernet and gigabit ethernet are the types of ethernet where fast ethernet is slower than gigabit ethernet and provide maximum data speed up to 100 Mbps.
The mini-map, as well as the main game screen, shows symbols denoting three kinds of entities: blue for allies, green for squadmates, and orange for enemies, this applies to all interactivity on the battlefield.  The top right displays kill notifications of all players in-game. On the Windows version of the game, the top left features a chat window when in multiplayer. Battlefield 4 options also allow colour-blind players to change the on-screen colour indicators to: tritanomaly, deuteranomaly and protanomaly.Weapon customisation is expansive and encouraged.
The top right displays kill notifications of all players in-game. On the Windows version of the game, the top left features a chat window when in multiplayer. Battlefield 4 options also allow colour-blind players to change the on-screen colour indicators to: tritanomaly, deuteranomaly and protanomaly.Weapon customisation is expansive and encouraged.
On the other hand, the gigabit ethernet has extended its speed at maximum to 1 Gbps by improving cabling technology, MAC layer, flow control protocols and quality of service.